float属性定义元素在哪个方向浮动。以往这个属性总应用于图像,使文本围绕在图像周围,不过在CSS中,任何元素都可以浮动。浮动元素会生成一个块级框,而不论它本身是何种元素。如果浮动非替换元素,则要指定一个明确的宽度;否则,它们会尽可能地窄
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| left | 元素向左浮动 |
| right | 元素向右浮动 |
| none | 默认值。元素不浮动,并会显示在其在文本中出现的位置 |
| inhert | 规定应该从父元素继承 float 属性的值 |
实例
<div class="main">
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<style>
.box{
float: left;
}
</style>
div是块级元素,在页面中独占一行,自上而下排列,也就是传说中的流
代码
<div class="box1">盒子1</div>
<div class="box2">盒子2</div>
<div class="box3">盒子3</div>
<div class="box4">盒子4</div>
<style>
div {height: 50px;}
.box1{width: 300px; background: red;}
.box2{width: 200px; background: green;}
.box3{width: 300px; background: yellow;}
.box4{width: 200px; background: blue;}
</style>
结果
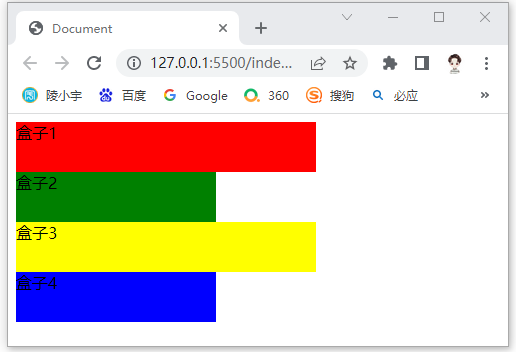
要在一行显示多个div,就需要脱离文档流,这就需要使用float浮动;
代码
<div class="box1">盒子1</div>
<div class="box2">盒子2</div>
<div class="box3">盒子3</div>
<div class="box4">盒子4</div>
<style>
div {height: 50px;}
.box1{width: 300px; background: red;}
.box2{width: 200px; background: green;float: left;}
.box3{width: 300px; background: yellow;}
.box4{width: 200px; background: blue; float: right;}
</style>
结果
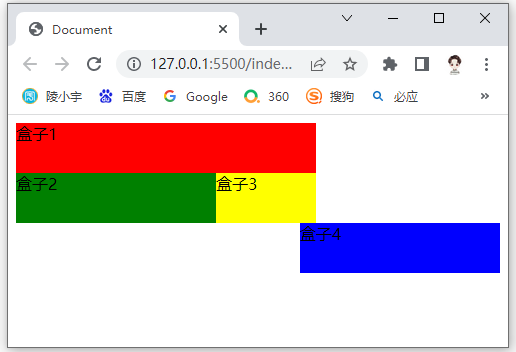
浮动可以理解为让某个div元素脱离标准流,漂浮在标准流之上,和标准流在不同的层次中
左浮动(float:left;),可以理解为漂浮起来后靠左排列,右浮动(float:right;)当然就是靠右排列
在使用float浮动后,浮动会给整个HTML布局带来一定的影响,所以必须要清除浮动
浮动会给整个HTML布局带来一定的影响,所以必须要清除浮动
属性值
clear只对本身起作用
实例
<div class="main">
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<div style="clear:both;"></div>
<style>
.box{
float: left;
}
</style>
当子元素的尺寸超过父元素的尺寸时,需要设置父元素显示溢出的子元素的方式,可在浮动元素的父级添加样式overflow:hidden;
属性值
实例
<div class="main">
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<style>
.main{overflow: hidden;}
.box{
float: left;
}
</style>
为了减少空标签的多余,可采用给父级的伪元素进行样式清除浮动
实例
<div class="main">
<div class="box"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
</div>
<style>
.main::after{
display: block;
content: "";
clear: both;
}
.box{
float: left;
}
</style>
*声明:内容来源于网络收集和整理,版权归原著所有,如来源信息有误或侵犯权益,请联系站长作修改和删除处理。